A team of researchers has unveiled a groundbreaking electrically programmable spintronic device that could change the game for AI hardware.
By leveraging spintronic technology, this innovation promises to boost computational performance while dramatically cutting power consumption—a huge step forward for energy-efficient artificial intelligence.
What Makes Spintronics Different?
Unlike traditional semiconductor-based circuits, spintronics doesn’t just rely on an electron’s charge—it takes advantage of its intrinsic spin to store and process data.
This means faster, more efficient computing, making spintronic devices a promising candidate for next-generation AI and neuromorphic computing.
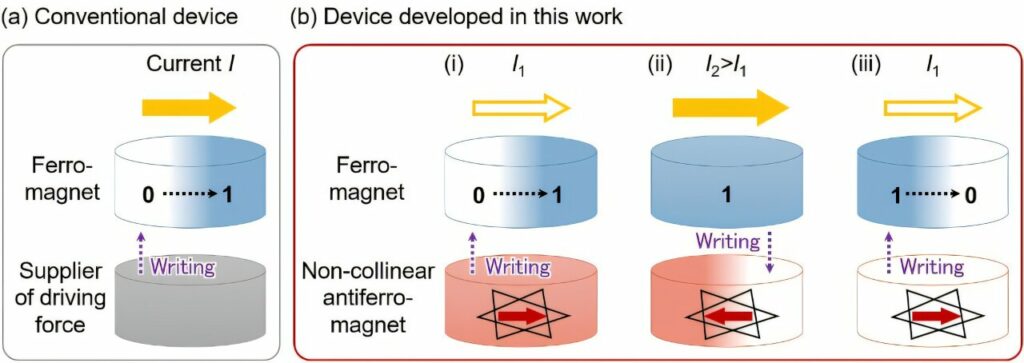
The big breakthrough here? The research team has created an electrically programmable spintronic component that can be reconfigured on the fly. That kind of flexibility is a major advantage for AI-driven tasks.
Why This Matters for AI Hardware
Today’s AI hardware largely depends on CMOS-based architectures, which are hitting roadblocks in terms of scaling and power efficiency.
This new spintronic device could sidestep those challenges, paving the way for smarter, more efficient hardware that keeps up with the increasing demand for deep learning and high-performance AI models.
By merging spintronics with electrical programmability, researchers hope to bridge the gap between traditional von Neumann computing and neuromorphic designs.
Some experts even believe this could make a real difference in reducing AI’s energy demands—an important consideration as machine learning systems grow ever more power-hungry.
The next phase of this project will focus on fine-tuning the device’s performance and exploring how it could be scaled for broader applications, such as AI inference and edge computing.
As the push for energy-efficient AI hardware continues, innovations like this electrically programmable spintronic technology could play a key role in shaping the industry’s future.